Sleep Apnea
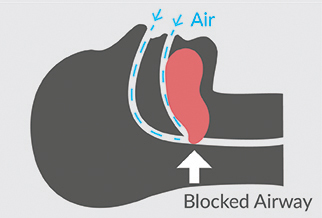
People with sleep apnea often snore loudly and can even stop breathing for short periods of time while sleeping. Sleep apnea occurs when tissue in the back of your throat collapses and blocks your airway, reducing the amount of oxygen being delivered to the rest of your body. This lack of oxygen causes you to briefly wake up, sometimes so quickly you don't even notice. This can happen hundreds of times in a single night, which may cause you to wake up feeling drowsy and unrefreshed.
Symptoms of sleep apnea include:
- Daytime sleepiness or fatigue
- Loud snoring
- Sudden awakenings accompanied by choking sounds or gasping for breath
- Morning headaches
- Dry mouth or sore throat upon awakening
- Frequent trips to the bathroom during the night
Sleep apnea can lead to numerous health issues, including increased risk for stroke and heart problems, diabetes, high blood pressure, weight gain, depression, irritability and accidents caused by daytime drowsiness. If you believe you may have sleep apnea, discuss your concerns with your dentist. Your dentist may refer you to a certified sleep specialist if more advanced testing is required.
Once diagnosed, there are several treatments for sleep apnea, including simple oral appliances, behavioral therapy and upper airway surgery.
Snoring
Snoring is an extremely common and usually harmless occurrence. Similar to sleep apnea, snoring is caused by soft tissue in the throat obstructing your airway, allowing you to continue breathing normally. The flow of air as you breathe causes the soft tissue to vibrate, generating the unmistakable sound of snoring, which comes out of either your nose, mouth or both.
Loud or excessive snoring can inhibit sleep for both yourself and a partner, leading to daytime drowsiness. There are several types of treatment for snoring, the most common include simple changes like sleeping in a new position or behavioral therapies like weight loss and alcohol avoidance. Oral appliances may be recommended in some cases. Extreme cases can occasionally require airway surgery.

